|
Table 5-1. Physical constants.
|
Quantity
|
Symbol, equation
|
Value
|
Uncert.
(ppb)
|
|
speed of light
|
c (see note *)
|
2.997 924 58´108 m s–1 (1010 cm s–1)
|
exact
|
|
Planck constant
|
h
|
6.626 068 76(52)´10–34 J s (10–27 erg s)
|
78
|
|
Planck constant, reduced
|
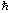 = h/2p = h/2p
|
1.054 571 596(82)´10–34 J s = 6.582 118 89(26)´10–22 MeV s
|
78,
39
|
|
electron charge magnitude
|
e
|
4.803 204 20(19)´10–10 esu = 1.602 176 462(63)´10–19 C
|
39,
59
|
|
conversion constant
|
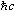
|
197.326 960 1(78) MeV fm (= eV nm)
|
39
|
|
electron mass
|
me
|
0.510 998 902(21) MeV/c2 = 9.109 381
88(72)´10–31 kg
|
40, 79
|
|
proton mass
|
mp
|
938.271 998(38) MeV/c2 = 1.672 621
58(13)´10–27 kg
|
40, 79
|
|
|
|
= 1.007 276 466 88(13) u = 1836.152 667 5(39) me
|
0.13,
2.1
|
|
deuteron mass
|
md
|
1875.612 762 (75) MeV/c2
|
40
|
|
unified atomic mass unit (u)
|
(mass 12C atom)/12 = (1 g)/(NA mol)
|
931.494 013(37) MeV/c2 = 1.660 538
73(13)´10–27 kg
|
40, 79
|
|
permittivity of free space
|
e0 = 1/(m0c2)
|
8.854 187 817¼´10–12 F m–1
|
exact
|
|
permeability of free space
|
m0
|
4p´10–7 N A–2 = 12.566
370 614¼´10–7 N A–2
|
exact
|
|
fine-structure constant
|
a = e2/4pe0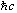
|
1/137.035 999 76(50)
|
3.7
|
|
classical electron radius
|
re = e2/4pe0mec2
|
2.817 940 285(31)´10–15 m
|
11
|
|
Bohr radius (mnucleus = ¥)
|
a0 = 4pe0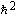 /mee2 = rea–2 /mee2 = rea–2
|
0.529 177 208 3(19)´10–10 m (10–8 cm)
|
3.7
|
|
Rydberg energy
|
hcR¥
= mee4/2(4pe0)2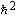
=mec2a2/2
|
13.605 691 72(53) eV
|
39
|
|
Thomson cross section
|
sT
= 8p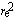 /3 /3
|
0.665 245 854(15) barn (10–28 m2)
|
22
|
|
Bohr magneton
|
mB = e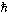 /2me /2me
|
5.788 381 749(43)´10–11 MeV T–1
|
7.3
|
|
nuclear magneton
|
mN = e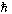 /2mp /2mp
|
3.152 451 238(24)´10–14 MeV T–1
|
7.6
|
|
electron cyclotron freq./field
|
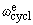 /B = e/me /B = e/me
|
1.758 820 174(71)´1011 rad s–1 T–1
|
40
|
|
proton cyclotron freq./field
|
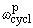 /B = e/mp /B = e/mp
|
9.578 834 08(38)´107 rad s–1 T–1
|
40
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 5-1. Physical constants(continued).
|
Quantity
|
Symbol, equation
|
Value
|
Uncert.
(ppb)
|
|
Avogadro constant
|
NA
|
6.022 141 99(47)´1023 mol–1
|
79
|
|
Boltzman constant
|
k
|
1.380 650 3(24)´10–23 J K–1 = 8.617
342(15)´10–5 eV K–1
|
1700
|
|
molar volume, ideal gas at STP
|
NAk (273.15 K)/(101 325 Pa)
|
22.413 996(39)´10–3 m3 mol–1
|
1700
|
|
p
= 3.141 592 653 589 793 238
|
e = 2.718 281 828 459 045 235
|
g = 0.577 215 664 901 532 861
|
|
The
meter is the length of the path traveled by light in vacuum during a time
interval of 1/299 792 458 of a second.
|
|
1 in. =
2.54 cm
|
1 newton =
105 dyne
|
1 eV/c2 = 1.782
662´10–33 g
|
1 coulomb =
2.997 924 58´109 esu
|
|
1 Å =
10–8 cm
|
1 joule =
107 erg
|
hc/(1
eV) = 1.239 842 mm
|
1 tesla =
104 gauss
|
|
1 fm =
10–13 cm
|
1 cal =
4.184 joule
|
1 eV/h
= 2.417 989´1014 Hz
|
1 atm =
1.013 25´106 dyne/cm2
|
|
1 barn =
10–24 cm2
|
1 eV =
1.602 176 5´10–12 erg
|
1 eV/k = 11
604.5 K
|
0°C =
273.15 K
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
![]()
![]()